Translating the Evidence into Practice
Translation - Moving the best evidence into professional practice. The purpose of translation is to provide the best outcomes and value, and lower risks to our patient population.
Steps involved in Translating the Evidence into Practice:
- Set the goals
- Assemble a team
- Develop a PLAN - determine key stakeholders, expertise & support
- Anticipate barriers & facilitators
- Measure/collect data - baseline, process, outcomes, expenses
- Gain support & approval
- Implement - DO - pilot roll-out, educate, support, navigate
- Monitor - STUDY - observe & measure
- Manage & Adjust - ACT - Adapt, Adopt or Abandon based on evidence
- Sustain & Grow - Share the results, get feedback, embed in standards or policies, spread more broadly
- Celebrate the work you have accomplished!
Knowledge to Action (KTA) Framework
The Knowledge to Action (KTA) Framework is used for facilitating the use of research knowledge by several stakeholders, such as practitioners, policymakers, patients and the public. The KTA process has two components: Knowledge Creation and Action.
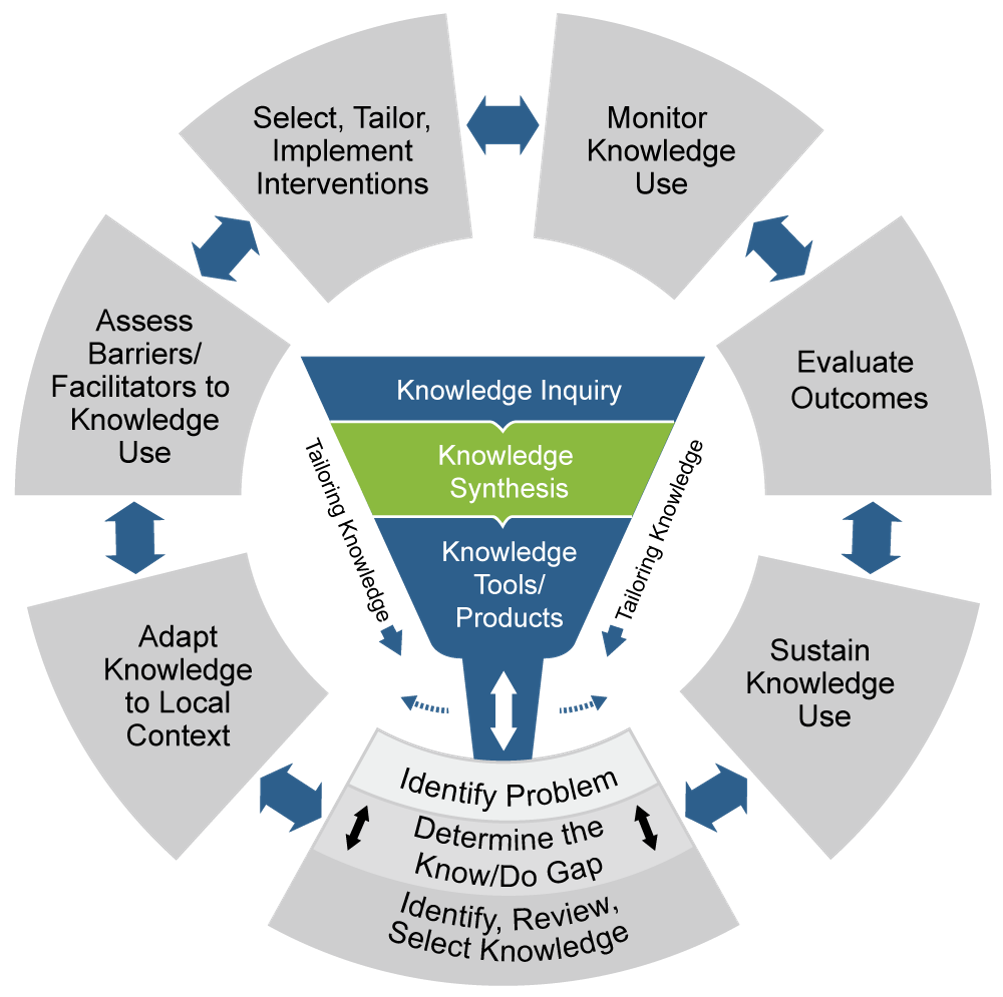
Adapted from Graham 2006 (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16557505/) by Crockett 2017 (https://medium.com/knowledgenudge/kt-101-the-knowledge-to-action-framework-7fbe399723e8)
Knowledge Creation includes knowledge inquiry, knowledge synthesis, and knowledge tools/products. Knowledge becomes more refined as it moves through these three steps.
Action includes identifying and appraising the problem and the known research, identifying barriers and successes, planning and executing, and finally monitoring, evaluating, and adjusting.
In summary, KTA is applying knowledge to real life situations.
Tools for Implementing Evidence and Managing Change
- JBI Manual for Evidence Implementation
- Tool 2G: Managing Change Checklist. AHRQ
- Appendix C: Example Implementation Plan. AHRQ
- Fineout-Overholt, E., Williamson, K. M., Gallagher-Ford, L., Melnyk, B. M., & Stillwell, S. B. (2011). Evidence-based practice, step by step: following the evidence: planning for sustainable change. AJN The American Journal of Nursing, 111(1), 54-60.
- Gesme, D., & Wiseman, M. (2010). How to implement change in practice. Journal of oncology practice, 6(5), 257–259. https://doi.org/10.1200/JOP.000089
- Institute for Healthcare Improvement. Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) Worksheet.
Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) is a useful tool for documenting a test of change. The PDSA cycle is shorthand for testing a change by developing a plan to test the change (Plan), carrying out the test (Do), observing and learning from the consequences (Study), and determining what modifications should be made to the test (Act).